Licenses are managed as Smart licenses from Cisco IOS XE Fuji 16.9.1 and later. Right-to-Use licenses are deprecated from Cisco IOS XE Fuji 16.9.1 .
CSSM enables you to manage all your Cisco smart software licenses from one centralized portal. With CSSM, you can organize and view your licenses in groups called virtual accounts (collections of licenses and product instances).
You can access the CSSM on https://software.cisco.com/#, by clicking the Smart Software Licensing link under the License tab.
Use a Chrome 32.0, Firefox 25.0, or Safari 6.0.5 web browser to access CSSM. Also, ensure that Javascript 1.5 or a later version is enabled in your browser.

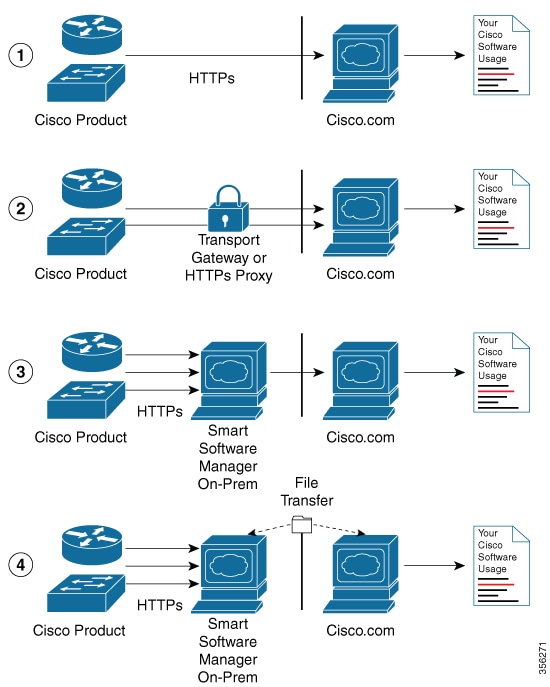
The following illustration shows the various options available to connect to CSSM:
Options 1 and 2 provide an easy connection option, and options 3 and 4 provide a secure environment connection option. Cisco Smart Software Manager On-Prem (formerly known as Cisco Smart Software Manager satellite) provides support for options 3 and 4.
The following section is required for those licenses that were purchased without a Cisco Smart Account. These licenses will not be available in CSSM after you have upgraded to Cisco IOS XE Fuji 16.9.1 . You are requested to contact the Cisco Global Licensing Operations (GLO) team with the following email template. Fill the template with the appropriate information to request linking of your existing licenses to your Cisco Smart Account in CSSM.
To: licensing@cisco.com
Subject: Request for Linking Existing Licenses to Cisco Smart Account
Cisco.com ID: #####
Smart virtual account name: #####
Smart account domain ID (domain in the form of "xyz.com"): #####
List of UDIs:
List of licenses with count:
Proof of purchase (Please attach your proof of purchase along with this mail)
The following sections provide information about how to set up a connection to CSSM and set up the license level.
The following steps show how to set up a Layer 3 connection to CSSM to verify network reachability. Skip this section if you already have Layer 3 connectivity to CSSM.
| Command or Action | Purpose |
|---|---|
Step 1 | enable |
Device> enableEnables privileged EXEC mode.
Enter your password, if prompted.
Device# configure terminalEnters global configuration mode.
Device(config)# ip name-server 209.165.201.1 209.165.200.225 209.165.201.14 209.165.200.230Configures Domain Name System (DNS).
Device(config)# ip name-server vrf Mgmt-vrf 209.165.201.1 209.165.200.225 209.165.201.14 209.165.200.230(Optional) Configures DNS on the VRF interface.
You should configure this command as an alternative to the ip name-server command.
Device(config)# ip domain lookup source-interface Vlan100(Optional) Configures the source interface for the DNS domain lookup.
Device(config)# ip domain name example.comConfigures the domain name.
Device(config)# ip host tools.cisco.com 209.165.201.30(Optional) Configures static hostname-to-address mappings in the DNS hostname cache if automatic DNS mapping is not available.
Device(config)# interface Vlan100 Device(config-if)# ip address 192.0.2.10 255.255.255.0 Device(config-if)# exit
Configures a Layer 3 interface.
Device(config)# ntp server 198.51.100.100 version 2 prefer
Forms a server association with the specified system.
The ntp server command is mandatory to ensure that the device time is synchronized with CSSM.
Device(config)# interface GigabitEthernet1/0/1 Device(config-if)# switchport access vlan 100 Device(config-if)# switchport mode access Device(config-if)# exit Device(config)#
(Optional) Enables the VLAN for which this access port carries traffic and sets the interface as a nontrunking nontagged single-VLAN Ethernet interface.
This step is to be configured only if the switchport access mode is required.
Device(config)# ip route 192.0.2.0 255.255.255.255 192.0.2.1
Configures a route on the device.
You can configure either a static route or a dynamic route.
Device(config)# license smart transport callhomeEnables the transport mode as Call Home.
The license smart transport callhome command is mandatory.
Device(config)# ip http client source-interface Vlan100Configures a source interface for the HTTP client.
The ip http client source-interface interface-type interface-number command is mandatory.
Device(config)# exit(Optional) Exits global configuration mode and returns to privileged EXEC mode.
Device# copy running-config startup-config(Optional) Saves your entries in the configuration file.
By default, the CiscoTAC-1 profile is already set up on the device. Use the show call-home profile all command to check the profile status.
The Call Home service provides email-based and web-based notification of critical system events to CSSM.
To configure and enable the Call Home service, perform this procedure:
| Command or Action | Purpose |
|---|---|
Step 1 | enable |
Device> enableEnables privileged EXEC mode.
Enter your password, if prompted.
Device# configure terminalEnters global configuration mode.
Device(config)# call-homeEnters Call Home configuration mode.
Device(config-call-home)# no http secure server-identity-checkDisables server identity check when HTTP connection is established.
Device(config-call-home)# contact-email-addr username@example.comAssigns customer's email address. You can enter up to 200 characters in email address format with no spaces.
Device(config-call-home)# profile CiscoTAC-1By default, the CiscoTAC-1 profile is inactive. To use this profile with the Call Home service, you must enable the profile.
Device(config-call-home-profile)# destination transport-method httpEnables the Call Home service via HTTP.
Device(config-call-home-profile)# destination address http https://tools.cisco.com/its/service/oddce/services/DDCEServiceConnects to CSSM.
Device(config-call-home-profile)# activeEnables the destination profile.
Device(config-call-home-profile)# no destination transport-method emailDisables the Call Home service via email.
Device(config-call-home-profile)# exitExits Call Home destination profile configuration mode and returns to Call Home configuration mode.
Device(config-call-home)# exitExits Call Home configuration mode and returns to global configuration mode.
Device(config)# service call-homeEnables the Call Home feature.
Device(config)# exitExits global configuration mode and returns to privileged EXEC mode.
Device# copy running-config startup-config(Optional) Saves your entries in the configuration file.
The Call Home service can be configured through an HTTPs proxy server. This configuration requires no user authentication to connect to CSSM.
Authenticated HTTPs proxy configurations are not supported.
To configure and enable the Call Home service through an HTTPs proxy, perform this procedure:
| Command or Action | Purpose |
|---|---|
Step 1 | enable |
Device> enableEnables privileged EXEC mode.
Enter your password, if prompted.
Device# configure terminalEnters global configuration mode.
Device(config)# call-homeEnters Call Home configuration mode.
Device(config-call-home)# contact-email-addr sch-smart-licensing@cisco.comConfigures the default email address as sch-smart-licensing@cisco.com.
Device(config-call-home)# http-proxy 198.51.100.10 port 3128Configures the proxy server information to the Call Home service.
Device(config-call-home)# profile CiscoTAC-1By default, the CiscoTAC-1 profile is inactive. To use this profile with the Call Home service, you must enable the profile.
Device(config-call-home-profile)# destination transport-method httpEnables the Call Home service via HTTP.
Device(config-call-home-profile)# no destination transport-method emailDisables the Call Home service via email.
Device(config-call-home)# profile test1Enters Call Home destination profile configuration mode for the specified destination profile name. If the specified destination profile does not exist, it is created.
Device(config-call-home-profile)# reporting smart-licensing-dataEnables data sharing with the Call Home service via HTTP.
Device(config-call-home-profile)# destination transport-method httpEnables the HTTP message transport method.
Device(config-call-home-profile)# destination address http https://tools.cisco.com/its/service/oddce/services/DDCEServiceConnects to CSSM.
Device(config-call-home-profile)# activeEnables the destination profile.
Device(config-call-home-profile)# exitExits Call Home destination profile configuration mode and returns to Call Home configuration mode.
Device(config-call-home)# exitExits Call Home configuration mode and returns to global configuration mode.
Device(config)# service call-homeEnables the Call Home feature.
Device(config)# ip http client proxy-server 198.51.100.10 port 3128Enables the Call Home feature.
Device(config)# exitExits global configuration mode and returns to privileged EXEC mode.
Device# copy running-config startup-config(Optional) Saves your entries in the configuration file.
For information about Cisco Smart Software Manager On-Prem (formerly known as Cisco Smart Software Manager satellite), see https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/buy/smart-accounts/software-manager-satellite.html.
To configure the Call Home service for the Cisco Smart Software Manager On-Prem (formerly known as Cisco Smart Software Manager satellite), perform this procedure:
| Command or Action | Purpose |
|---|---|
Step 1 | enable |
Device> enableEnables privileged EXEC mode.
Enter your password if prompted.
Device# configure terminalEnters global configuration mode.
Device(config)# call-homeEnters Call Home configuration mode.
Device(config-call-home)# no http secure server-identity-checkDisables server identity check when HTTP connection is established.
Device(config-call-home)# profile test1Enters Call Home destination profile configuration mode for the specified destination profile name. If the specified destination profile does not exist, it is created.
Device(config-call-home-profile)# reporting smart-licensing-dataEnables data sharing with the Call Home service via HTTP.
Device(config-call-home-profile)# destination transport-method httpEnables the HTTP message transport method.
Device(config-call-home-profile)# destination address http https://209.165.201.15:443/Transportgateway/services/DeviceRequestHandler Device(config-call-home-profile)# destination address http http://209.165.201.15:80/Transportgateway/services/DeviceRequestHandlerConfigures the destination URL (CSSM) to which Call Home messages are sent.
Note
Ensure the IP address or the fully qualified domain name (FQDN) in the destination URL matches the IP address or the FQDN as configured for the Satellite Name on the Cisco Smart Software Manager On-Prem.
Device(config-call-home-profile)# destination preferred-msg-format xml(Optional) Configures a preferred message format. The default is XML.
Device(config-call-home-profile)# activeEnables the destination profile. By default, a profile is enabled when it is created.
Device(config-call-home-profile)# exitExits Call Home destination profile configuration mode and returns to Call Home configuration mode.
Device(config-call-home)# exitExits Call Home configuration mode and returns to global configuration mode.
Device(config)# ip http client source-interface Vlan100Configures a source interface for the HTTP client.
The ip http client source-interface interface-type interface-number command is mandatory for a vrf interface.
Device(config)# crypto pki trustpoint SLA-TrustPoint(Optional) Declares the trustpoint and a given name and enters ca-trustpoint configuration mode.
Device(ca-trustpoint)# revocation-check none(Optional) Specifies that certificate checking is ignored.
Device(ca-trustpoint)# end(Optional) Exits ca-trustpoint configuration mode and returns to privileged EXEC mode.
Device# copy running-config startup-config(Optional) Saves your entries in the configuration file.
| Command or Action | Purpose |
|---|---|
Step 1 | enable |
Device> enableEnables privileged EXEC mode.
Enter your password, if prompted.
Device# configure terminalEnters global configuration mode.
Device(config)# license boot level network-essentialsActivates the licenses on the switch.
Device(config)# exitReturns to the privileged EXEC mode.
Device# write memorySaves the license information on the switch.
Device# show version ------------------------------------------------------------------------------ Technology-package Current Type Technology-package Next reboot ------------------------------------------------------------------------------ network-essentials Smart License network-essentials None Subscription Smart License None Shows license-level information.
Device# reloadReloads the device.
Downgrading a device from Cisco IOS XE Fuji 16.9.1 to any prior release will migrate the smart license to traditional license. All smart license information on the device will be removed. In case the device needs to be upgraded back to Cisco IOS XE Fuji 16.9.1 , the license status will remain in evaluation mode until the device is registered again in CSSM.
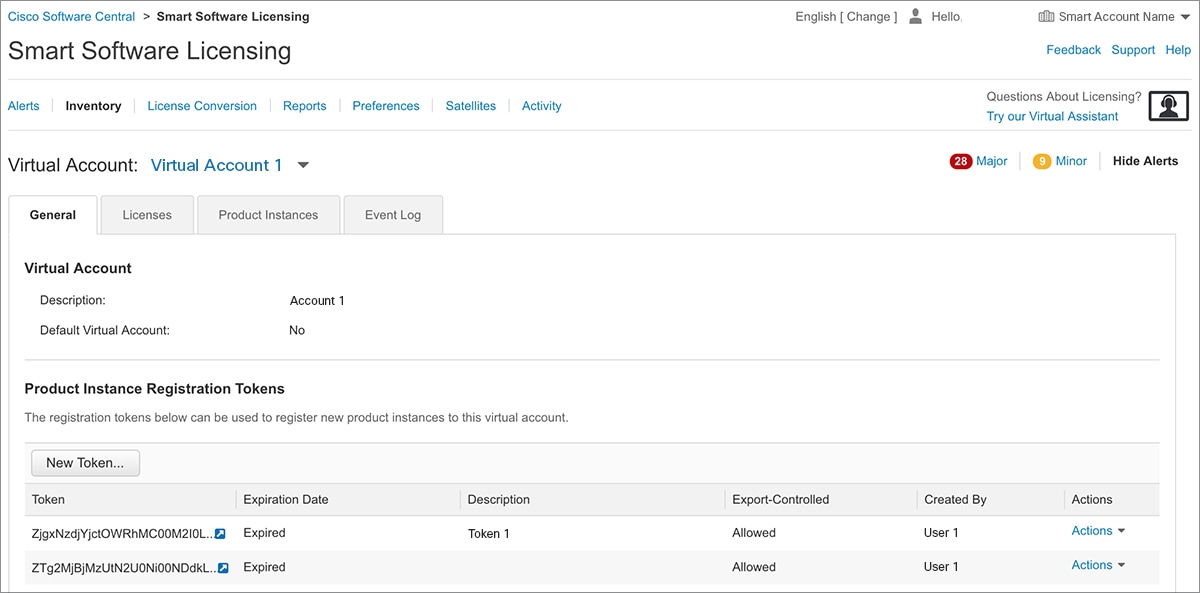
You must log in to the portal using the username and password provided by Cisco.
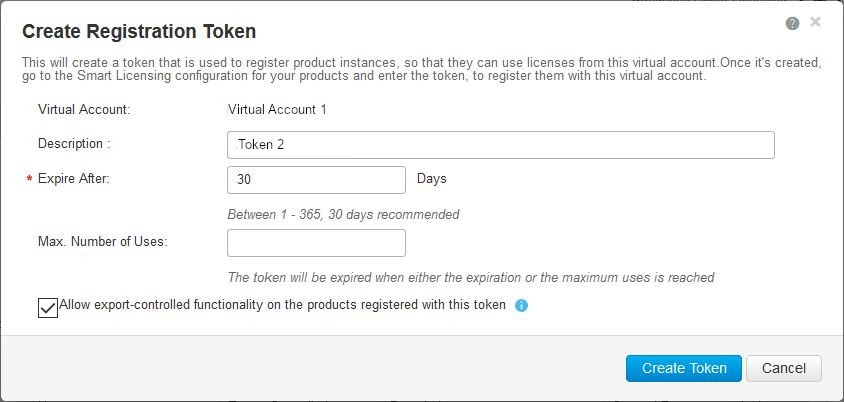
Enabling this checkbox ensures Cisco compliance with US and country-specific export policies and guidelines. For more information, see https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/about/legal/global-export-trade.html.
To register a device with the new token, perform this procedure:
| Command or Action | Purpose |
|---|---|
Step 1 | enable |
Device> enableEnables privileged EXEC mode.
Enter your password, if prompted.
Device# license smart register idtoken $Tl4UytrNXBzbEs1ck8veUtWaG5abnZJOFdDa1FwbVRa%0AblRMbz0%3D%0A Registers the device with the back-end server using the token generated from CSSM.
Device# write memorySaves the license information on the device.
To verify the status of a license after registration, use the show license all command.
Device> enable Device# show license all Smart Licensing Status ====================== Smart Licensing is ENABLED Registration: Status: REGISTERED Smart Account: Smart Account Name Virtual Account: Virtual Account 1 Export-Controlled Functionality: Allowed Initial Registration: SUCCEEDED on Jul 16 09:44:50 2018 IST Last Renewal Attempt: None Next Renewal Attempt: Jan 12 09:44:49 2019 IST Registration Expires: Jul 16 09:39:05 2019 IST License Authorization: Status: AUTHORIZED on Jul 31 17:30:02 2018 IST Last Communication Attempt: SUCCEEDED on Jul 31 17:30:02 2018 IST Next Communication Attempt: Aug 30 17:30:01 2018 IST Communication Deadline: Oct 29 17:24:12 2018 IST Export Authorization Key: Features Authorized: Utility: Status: DISABLED Data Privacy: Sending Hostname: yes Callhome hostname privacy: DISABLED Smart Licensing hostname privacy: DISABLED Version privacy: DISABLED Transport: Type: Callhome License Usage ============== C9500 48Y4C DNA Advantage (C9500-DNA-48Y4C-A): Description: C9500 48Y4C DNA Advantage Count: 1 Version: 1.0 Status: AUTHORIZED Export status: NOT RESTRICTED C9500 48Y4C NW Advantage (C9500-48Y4C-A): Description: C9500 48Y4C NW Advantage Count: 1 Version: 1.0 Status: AUTHORIZED Export status: NOT RESTRICTED Product Information =================== UDI: PID:C9500-48Y4C,SN:CAT2150L5HK Agent Version ============= Smart Agent for Licensing: 4.5.2_rel/32 Component Versions: SA:(1_3_dev)1.0.15, SI:(dev22)1.2.1, CH:(rel5)1.0.3, PK:(dev18)1.0.3 Reservation Info ================ License reservation: DISABLED
When your device is taken off the inventory, shipped elsewhere for redeployment, or returned to Cisco for replacement using the return merchandise authorization (RMA) process, you can use the deregister command to cancel the registration of your device.
To cancel device registration, follow this procedure:
Layer 3 connection to CSSM must be available to successfully deregister the device.
| Command or Action | Purpose |
|---|---|
Step 1 | enable |